Table Of Content

Sleek dark-themed site for an LA-based artist management, touring & studio collective -- Beehive. Wearing a wedge simply feels more stable on the foot due to even weight distribution, making them easier to walk in. An untrained stiletto wearer might feel a little wobbly when walking or even standing still, while the wider base of a wedge—and the slightly shorter height—encourages easier, more comfortable and more balanced upright movement.
Designing a stepped wedge trial: three main designs, carry-over effects and randomisation approaches
The result is a home that, like so many well-designed modern homes of the era, is a masterstroke of architecture that offers an almost seamless blend of interior and exterior spaces with an open plan that allows for natural light from all sides as well as the vaulted ceiling. CSH 20(B) is also a brilliant testament that functional and attractive design can be achieved on a relatively modest budget. It’s a wonderful house that’s still there today, although I believe the barrel-vaulted roof has been replaced with a flat one. The authors acknowledge the help of Alan Girling and Prakash Patil, who contributed to discussions regarding this paper. Since then, I fell in love with & have been primarily using React & Redux in web applications.
Reporting of stepped wedge cluster randomised trials
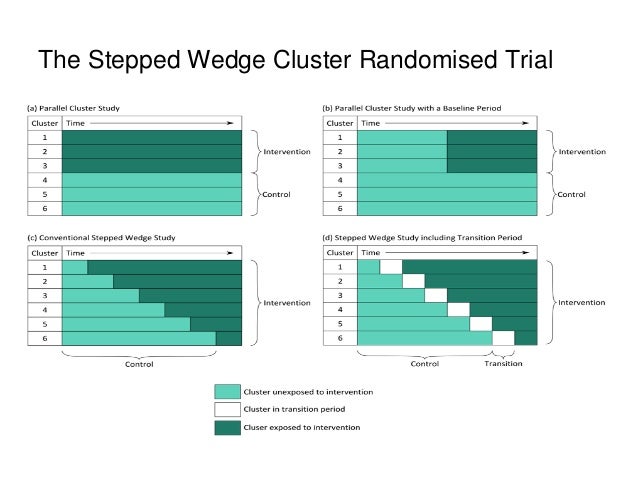
Finally, three out of four SW-CRTs in Table 3 adopted the linear or generalized linear mixed models for the design and analysis, whereas our methodological review suggests that marginal models are viable alternatives for designing and analyzing SW-CRTs. Application of marginal models to future neurosurgical SW-CRTs can be based on software tools listed in Table 1 and and22. In a standard parallel trial the intervention is allocated to some clusters and not to others and analysis compares intervention arms. In a stepped wedge study, exposed (intervention) and unexposed (control) observation periods take the place of “arms” in parallel cluster trials. Thus, the distribution of results across unexposed observation periods is compared with that across the exposed observation periods. As with any randomised comparison, characteristics of the individuals and clusters should be summarised by exposure status so as to allow consideration of selection biases and lack of balance.
Sample Size Determination
Randomised Controlled Trials (RCTs) are considered the 'Gold Standard' test of clinical effectiveness [1] and such trials are increasingly being used in evaluations of non-clinical interventions. There are many ways of classifying RCTs, such as the extent of blinding, method of randomisation (including whether interventions will be randomised at individual or cluster level) and the inclusion (or not) of a preference arm [2]. A further classification is the way in which participants are exposed to the intervention [2] and we refer to this as the 'design' of the RCT. This paper provides a review of studies employing a particular design, known as a 'stepped wedge'.
Love Beauty and Planet Blooming Color Murumuru Butter & Rose Conditioner
Carry-over effects can also arise at the cluster level in trials comparing methods to detect a health condition and change its management. In such a scenario, the number of undetected cases remaining in clusters may decline over time. The types of undetected cases may also change, for example because cases that are more challenging to identify might remain undetected longer. The intervention and control conditions could therefore differ in how effectively cases are detected, and these changes over time will be influenced by the duration of the control condition.
In this example, even though the numbers of clusters were unequal across strata, they were multiples of each other and at least one cluster from each stratum switched to intervention at each crossover point. This feature makes it feasible to include categorical time effects in the analysis that can be shared across strata, and hence simplifies the analysis. One trial protocol found in our review describes a more complex stratification, where some strata will have only two steps and the SWT conducted within strata may not overlap in time, resulting in a complex data structure and analysis [19]. Fuller et al. investigated the effect that providing feedback about hand hygiene to doctors and nurses would have on their compliance with protocol [11].
Power Calculations for Stepped Wedge Designs with Binary Outcomes: Methods and Software
In such trials we consider outcome data from individuals exposed before, during, or after rollout to be ‘collected’ before, during, or after rollout. The value of the principle of randomization to compare treatments and interventions remains undisputed in medical research, and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are the acknowledged gold standard. Due to practical considerations, a number of variations have been developed in addition to the traditional RCT design, including cluster-randomized trials and the stepped-wedge design (SWD). In cluster-randomized, parallel-group trials—the prevailing type of cluster-randomized trial—groups of individuals (e.g. doctors’ practices, school classes, regions), rather than individuals themselves, are randomized to receive the intervention.
An integrated approach to health, wellbeing, and productivity at work: a design of a stepped wedge worksite ... - BMC Public Health
An integrated approach to health, wellbeing, and productivity at work: a design of a stepped wedge worksite ....
Posted: Fri, 02 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Design choice one: number and length of steps
If given these, a number of steps and step length can be found where the total trial duration is satisfactory and required sample size can be achieved, given the number of clusters considered, then the selections are finalised. This process can be iterative because the sample size required will depend on the number of steps [7]. Options described in the next section can be considered if there are no satisfactory selections of step length or duration.
Significance testing, power, and sample size planning
Some of the brands we selected—including Crocs, Vionic and Sorel—are reader favorites and are frequently worn by our editors. Many high-scoring styles have special comfort features, like multi-density foam padding, built into their designs. To further vet our picks, we read real customer reviews and approached every pick with a discerning eye, focusing not only on comfort level, but also fashion versatility, construction and overall price.
Wedges also commonly have added padding in the footbed—or a foam material in the wedge shape itself—that’s designed to further absorb impact. We’ve covered wide-spanning topics—including the most comfortable heels and the best sandals for plantar fasciitis—analyzing wearability, quality, value and aesthetics. Through hours of critical assessment, research, reading reviews and testing products, our goal is to help you make smart shopping decisions whether you’re looking for footwear, clothing or accessory ideas. FitFlop’s Eloise Slides are easy to slip into, while the wide crossover straps and cork-wrapped sole add a statement-making look.
We have included three studies of this nature in this review [12,14,17] although it is questionable whether studies with only two steps should be considered as stepped wedge designs. Figure Figure22 shows the results of our search which identified only 12 papers or protocols (referred to as studies) in which a stepped wedge design was described. Three of the included studies [12-14] are protocols describing trials that were being designed or implemented rather than providing results of the evaluation. Basic information about each of the included studies is shown in Tables Tables1,1, ,2,2, ,33. The review includes studies based on both individual and cluster allocations and is not restricted to RCTs.
In case study one it appears that the intervention has minimal implementation lag, and there are no restrictions on the number of steps, so the trial could be designed with the maximum number of steps, and step length set simply with the total trial duration and hence sample size in mind. In case study two, though a closed cohort, outcome data are obtained routinely so there are no restrictions on the number of steps arising from cost or measurement burden. The number of steps was, however, constrained to be no more than four by the preference to implement the intervention only at the start of school terms and conduct the trial in one school year, and step length was likewise constrained to be the length of the school term. With careful advance planning and publicity for the intervention, there need not be any implementation lag in case study two, and neither does it seem likely there would be any further delay for the intervention (providing breakfast) to affect the outcome (school attendance).
Design, implementation, and inferential issues associated with clinical trials that rely on data in electronic medical ... - BMC Medical Research Methodology
Design, implementation, and inferential issues associated with clinical trials that rely on data in electronic medical ....
Posted: Thu, 16 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
However, given that most policies are rolled out over a period of time, the stepped wedge cluster randomised trial offers a fair (as the order of the rollout is determined at random) and randomised evaluation. Policy makers ought to take advantage of this pragmatic study design to evaluate effectiveness of policy changes. Recruitment of individual participants is not typically necessary when policy or service delivery interventions are studied, and where cross-sectional designs based on anonymous data, such as death and morbidity rates, are used (as in example 4). Particular care is needed, however, when individuals are recruited within each cluster to take part in the study. Here, as in the case of parallel designs, steps should be taken to mitigate the risk that participants will vary systematically across exposed and unexposed observation periods.
Three of the included studies [12–14] are protocols describing trials that were being designed or implemented rather than providing results of the evaluation. Designs such as the continuous recruitment short exposure are more robust than the open or closed cohort designs because each individual experiences only one condition, so carry-over effects are less likely. Outcomes under the intervention condition are estimated only from individuals with no prior exposure to the control.
First, it may be the case that a key stakeholder (such as hospital manager or government minister) thinks that there is already sufficient evidence of effectiveness, whereas the researcher might take a different view. For example, when the UK government announced a new flagship programme called Sure Start to provide support for preschool children in deprived neighbourhoods, there was already some evidence in favour of the intervention,5 6 7 but value for money had not been proven to everyone’s satisfaction. Wedges have a wider surface area that spreads weight throughout your whole foot, while a heel’s design focuses weight on a tiny point on the heel, which can cause foot pain and discomfort. Since a wedge spreads your weight across the entire foot, you can also comfortably wear them longer.





















